大佬教程收集整理的这篇文章主要介绍了Java工程师的进阶之路,大佬教程大佬觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。
public class Sort {
public static void @H_250_49@main(String[] args) {
testTime();
testSort();
}
public static void testTime() {
int[] arr = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (@H_184_38@math.random() * 100 + 1);
}
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
// bubbleSort(arr);
// SELEctionSort(arr);
// insertionSort(arr);
// sHellSort(arr);
// quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
// mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
// radixSort(arr);
// counTingSort(arr);
// heapSort(arr);
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((e - s) + "ms");
}
public static void testSort() {
int[] arr = new int[50];
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (@H_184_38@math.random() * 100 + 1);
}
// bubbleSort(arr);
// SELEctionSort(arr);
// insertionSort(arr);
// sHellSort(arr);
// quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
// mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
// radixSort(arr);
// counTingSort(arr);
// heapSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
//堆排序(大顶堆:升序算法c;小顶堆:降序算法)
public static void heapSort(int arr[]) {
//创建大顶堆
for (int i = arr.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapAdjust(arr, i, arr.length);
}
//调整大顶堆
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
//交换元素
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
//调整新堆
heapAdjust(arr, 0, i);
}
}
//堆调整
public static void heapAdjust(int arr[], int ci, int length) {
//缓存当前结点
int temp = arr[ci];
//开始循环调整
for (int li = ci * 2 + 1; li < length; li = li * 2 + 1) {
//说明左子结点的值小于右子结点的值
if (li + 1 < length && arr[li] < arr[li + 1]) {
li = li + 1;
}
//说明当前子结点的值大于父结点的值
if (arr[li] > temp) {
arr[ci] = arr[li];
ci = li;
} else {
break;
}
}
//放到调整位置
arr[ci] = temp;
}
//计数排序:升序算法
public static void counTingSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) return;
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) max = arr[i];
if (arr[i] < min) min = arr[i];
}
//统计次数
int[] counts = new int[@H_817_35@max - min + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
counts[arr[i] - min]++;
}
//累加次数
for (int i = 1; i < counts.length; i++) {
counts[i] += counts[i - 1];
}
//倒着重排
int[] newArr = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newArr[--counts[arr[i] - min]] = arr[i];
}
//复制数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = newArr[i];
}
}
//基数排序:升序算法
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) return;
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) max = arr[i];
if (arr[i] < min) min = arr[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] -= min;
}
int maxLength = String.valueOf(@H_817_35@max - min).length();
int[][] bucket = new int[10][arr.length];
int[] buckeTindex = new int[10];
for (int rounds = 0, base = 1; rounds < maxLength; rounds++, base *= 10) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int digit = arr[i] / base % 10;
bucket[digit][buckeTindex[digit]++] = arr[i];
}
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < buckeTindex.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < buckeTindex[i]; j++) {
arr[pos++] = bucket[i][j];
}
buckeTindex[i] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] += min;
}
}
//归并排序:升序算法
public static void @H_250_49@mergeSort(int[] arr, int L, int R, int[] temp) {
if (L >= R) return;
int tIdx = L, left = L, middle = (L + R) / 2, right = middle + 1;
@H_250_49@mergeSort(arr, L, middle, temp);
@H_250_49@mergeSort(arr, right, R, temp);
while (left <= middle && right <= R) {
if (arr[left] <= arr[right]) {
temp[tIdx++] = arr[left++];
} else {
temp[tIdx++] = arr[right++];
}
}
while (left <= middle) temp[tIdx++] = arr[left++];
while (right <= R) temp[tIdx++] = arr[right++];
for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i];
}
}
//快速排序:升序算法
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) return;
int left = L, right = R, pivot = arr[L];
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && arr[right] >= pivot) right--;
arr[left] = arr[right];
while (left < right && arr[left] <= pivot) left++;
arr[right] = arr[left];
}
arr[left] = pivot;
quickSort(arr, L, left - 1);
quickSort(arr, left + 1, R);
}
//希尔排序:升序算法
public static void sHellSort(int[] arr) {
for (int step = arr.length / 2; step > 0; step /= 2) {
for (int i = step; i < arr.length; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
int j = i - step;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp) {
arr[j + step] = arr[j];
j -= step;
}
arr[j + step] = temp;
}
}
}
//插入排序:升序算法
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j -= 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
//选择排序:升序算法
public static void SELEctionSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[@H_817_35@minIndex] > arr[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (@H_817_35@minIndex != i) {
int temp = arr[@H_817_35@minIndex];
arr[@H_817_35@minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
}
//冒泡排序:升序算法
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
递归版:
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
return binarySearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, target);
}
private static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int left, int right, int target) {
while (left <= right) {
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (target < arr[@H_817_35@middle]) {
right = middle - 1;
} else if (target > arr[@H_817_35@middle]) {
left = middle + 1;
} else {
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
迭代版:
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
return binarySearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, target);
}
private static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int left, int right, int target) {
if (left > right) return -1;
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
if (target < arr[@H_817_35@middle]) {
return binarySearch(arr, left, middle - 1, target);
} else if (target > arr[@H_817_35@middle]) {
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, right, target);
} else {
return middle;
}
}
树结点:
class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode() {}
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
递归版:
//中左右
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
//左中右
public static void @H_250_49@midOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
@H_250_49@midOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
@H_250_49@midOrder(root.right);
}
//左右中
public static void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
迭代版:
//中左右 => 右左(中空)
public static void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);
if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
} else {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
}
//左中右 => 右(中空)左
public static void @H_250_49@midOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);
} else {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
}
//左右中 => (中空)右左
public static void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
stack.push(null);
if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);
if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);
} else {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
}
层序遍历:
public static void layerOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
执行流程:

生命周期:

循环依赖:
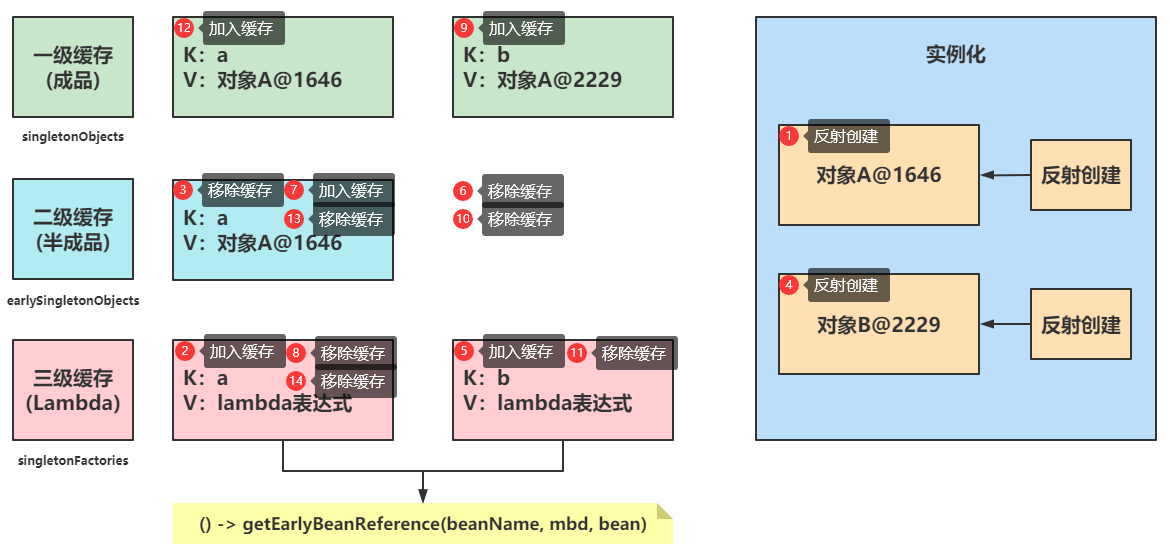
| 名称 | 完整定义 | 存储类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 一级缓存 | private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256); | 成品对象 |
| 二级缓存 | private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16); | 半成品对象 |
| 三级缓存 | private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16); | lambda表达式 |
1、如果只有一级缓存能否解决循环依赖问题?
如果只有一级缓存的话c;那就意味着成品对象和半成品对象都要放到一级缓存中c;在获取对象的时候c;就有可能获取到半成品对象c;而这个半成品对象是不能直接使用的c;因此需要使用一级缓存存放成品对象c;用二级缓存存放半成品对象。
2、只有一级二级缓存能否解决循环依赖问题?
只有一级二级缓存可以解决循环依赖问题c;但是这个是有前提条件的c;前提是不使用AOPc;如果开启了AOPc;那么Spring将会创建代理对象c;如果存在代理对象循环依赖问题任然存在。
3、那么问题又来了c;为什么需要三级缓存呢?
三级缓存是为了解决代理过程中的循环依赖问题。
4、使用代码演示一下循环依赖执行整个流程?

<bean id="a" class="io.github.caochenlei.domain.A">
<property name="b" ref="b"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="b" class="io.github.caochenlei.domain.b">
<property name="a" ref="a"></property>
</bean>
public class ABTest {
public static void @H_250_49@main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ab.xml");
A a = applicationContext.getBean(A.class);
System.out.println(a);
B b = applicationContext.getBean(B.class);
System.out.println(b);
}
}

暂未更新


以上是大佬教程为你收集整理的Java工程师的进阶之路全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决Java工程师的进阶之路所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得大佬教程网站内容还不错,欢迎将大佬教程推荐给程序员好友。
本图文内容来源于网友网络收集整理提供,作为学习参考使用,版权属于原作者。
如您有任何意见或建议可联系处理。小编QQ:384754419,请注明来意。